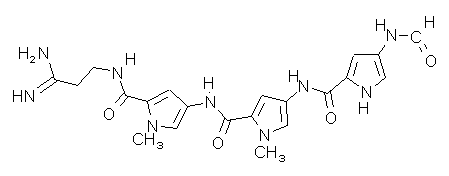

| Name | Distamycin A.HCl
Stallimycin 3-[1-methyl-4-[1-methyl-4-[1-methyl-4-(formylamino)pyrrole-2-carboxamido]- pyrrole-2-carboxamido]pyrrole-2-carboxamide]propionamidine hydrochloride |
| MW | 517.975 |
| CAS# | 636-47-5 |
| Category | Pyrrolocarboxamide |
| Binding Mode | At low concentration, binds minor groove as monomer, at higher (eg, 2-4mM) binds as side-by-side antiparallel dimer. X-ray crystal structures of both binding mode have been acquired [Coll, 1987; Pelton, 1989] |
| Site Specificity | Minimal binding site: 5'-WWWW-6' [Coll, 1987], A/T preference based on MPE-Fe(II) and DNase I footprints [van Dyke, 1982; Fox, 1984] |
| Effect on DNA | Monomer binding has little effect on DNA conformation in x-ray crystal structure [Coll, 1987]. |
| Source | Originally isolated from Streptomyces distallicus [Di Marco, 1962 #943] later made by total synthesis [Arcamone, 1964]. |
| Preparation and Use | Prepared in ddH2O. Extinction coefficient 3.70x104 M-1 cm-1 at 303nm [Arcamone, 1964] . Some suggest that solutions of distamycin should be made fresh each time, as freezing reduces distamycin potency [Dattagupta, 1980;Bruzik, 1987; Pelton, 1989]. Protect from light and moisture; powder is very hygroscopic. |
| DNA drugs |
| Heme-Onc |
| Netscut Home |