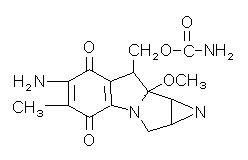

| Name | Mitomycin C
mutamycin mitocin C |
| CAS# | 50-07-7 |
| MW | 334.33 |
| Binding Mode | Reduced drug forms monofunctional covalent adducts and bifunctional interstrand crosslinks [Iyer, 1964] to N2-G [Tomasz, 1986] located in minor groove. Acid activated-mitomycin forms adduct with N7-G [Tomasz, 1987] in major groove. |
| Site Specificity | Adducts to guanines. 5'-CG-3' required for interstrand crosslink formation, and 5'-GG-3' required for intrastrand crosslinks. Preferred monofunctional site is 5'-CGN-3' > 5'-GGN-3', N is (C>T>G>A) according to study with oligonucleotides [Kumar, 1992]. |
| Effect on DNA | Monoadduct and interstrand crosslink do not significantly alter DNA conformation [Tomasz, 1987]; however, G-G intrastrand crosslink results in DNA bending [Kumar, 1992]. |
| Preparation and Use | Purple solution. Requires reduction for covalent bonding to DNA. Mitomycin C that is reduced and reoxidized is inactive [Iyer, 1964]. Activation with Na2S2O4 results primarily in G-G interstrand crosslinks, while enzymatic or Pt-catalyzed reduction results in monoadduct formation [Tomasz, 1987]. |
| DNA drugs |
| Heme-Onc |
| Netscut Home |